Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): The Ultimate Guide for Modern Marketers
You have the data, plenty of it. From your email platform to your website analytics, CRM, mobile app, and maybe even your call center, each piece tells part of your customer’s story. But the problem is clear: those pieces don’t always talk to each other.
Welcome to the fragmented state of customer data.
Marketers today are drowning in information while struggling to act on it. In fact, 47% of marketers say that some portion of their customer data remains siloed and hard to access.
One platform may hold behavioral data, another stores transactions, while a third manages support tickets. The result? Disjointed messages, missed opportunities, and campaigns that fall flat because they aren’t grounded in a complete understanding of the customer.
If you’ve ever tried to stitch together web analytics, email engagement, and transaction data into a meaningful customer view, you know how messy it can get. That’s exactly why Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) were born. A CDP is a marketer-managed system that unifies data from all your sources, online and offline, into a single, persistent customer profile.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about CDPs: what is a Customer Data Platform, how it works, benefits, real-world applications, how it compares to other tools, and how to choose and implement the right one. If you’re ready to move from fragmented tactics to unified strategy, you’re in the right place.
TL;DR:
Marketers are swimming in customer data—but most of it is scattered across disconnected tools. A Customer Data Platform (CDP) solves this by unifying all your first-party data into real-time customer profiles you can actually act on.
- CDP Definition: A marketer-managed system that unifies data from all sources into persistent, real-time customer profiles
- How It Works: Ingests data → Resolves identity → Unifies profiles → Builds segments → Activates across channels → Learns and optimizes
- Key Benefits: Smarter personalization, cross-channel orchestration, predictive insights, and reduced data silos
- How It Differs: Unlike CRMs and DMPs, CDPs handle real-time behavioral data and are built for activation
- Use Cases: Cart abandonment, dynamic recommendations, churn prediction, loyalty campaigns, personalized onboarding
What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
According to the CDP Institute, A Customer Data Platform is a “packaged software that creates a persistent, unified customer database that is accessible to other systems.” Think of it as the foundation that powers smarter segmentation, personalization, and cross-channel coordination.
Unlike traditional IT-built systems, CDPs are designed to be owned and operated by marketing teams, making it easier to turn data into action. A CDP is a real-time decision engine. It allows marketers to operate with agility, speed, and precision, using data to inform campaigns, predict behaviors, and personalize engagement.
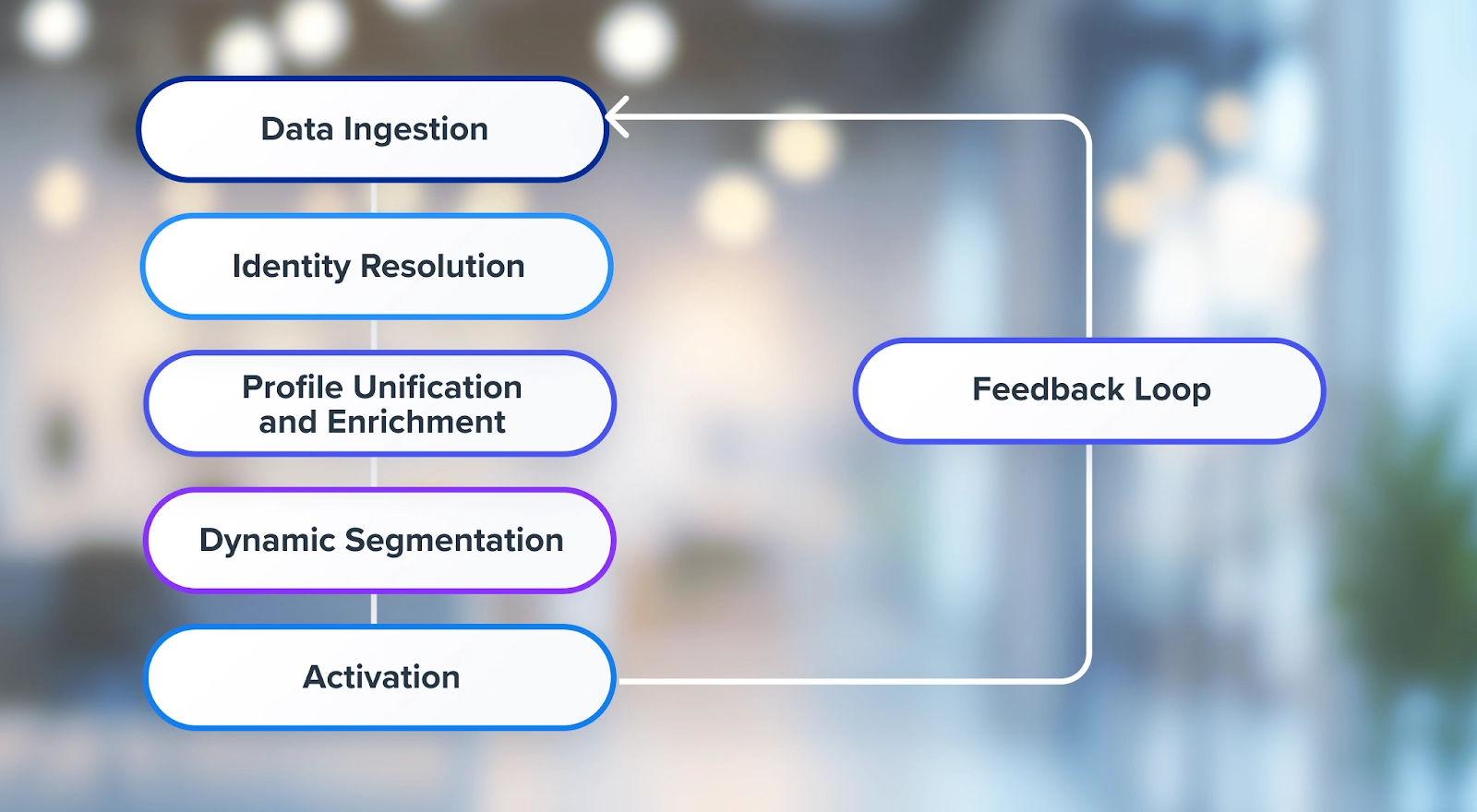
How a Customer Data Platform Works: From Data to Action
At first glance, a Customer Data Platform (CDP) may sound like another place to store customer information, but its true power lies in what it does with that data. A CDP is not just a database; it’s an intelligent engine that ingests raw signals, resolves identities, builds real-time profiles, and activates campaigns across channels. Let’s explore how it works, step by step.
1. Data Ingestion: Connecting Every Touchpoint
The CDP starts by pulling in data from a wide range of sources: website visits, mobile app activity, in-store transactions, CRM records, POS systems, email platforms, and even support interactions. This can happen via SDKs, APIs, batch imports, or cloud connectors. The data may be structured or unstructured, regardless, it’s captured and normalized into a consistent format.
2. Identity Resolution: Unifying Customer Journeys
One of the most valuable capabilities of a CDP is identity resolution. Whether your customer starts as anonymous (e.g., browsing on mobile) or known (e.g., logged into an account), the CDP stitches their actions together across devices and sessions. It uses identifiers like cookies, email addresses, device IDs, and user logins to build a single, persistent customer profile.
3. Profile Unification and Enrichment
Once identities are resolved, the CDP consolidates every known interaction into a unified profile. Each time a user takes an action, clicking a product, making a purchase, abandoning a cart, their profile updates in real time. Profiles can also include predictive attributes like likelihood to convert or churn, based on behavioral signals.
4. Dynamic Segmentation: Intelligence in Real Time
With profiles in place, marketers can build and maintain dynamic segments based on real-time activity, historical behavior, preferences, and predictions. These segments continuously evolve as new data flows in, no manual updates required. You can target frequent buyers, lapsed users, VIPs, or any audience you define.
5. Activation: Powering Personalized Engagement
The CDP integrates with your marketing channels, email platforms, ad networks, SMS tools, push notification systems, to activate campaigns using the most up-to-date customer data. This ensures that every message is contextually relevant and consistent across channels.
6. Feedback Loop: Learning and Optimizing
Finally, CDPs close the loop by capturing campaign results and feeding performance metrics back into the system. This helps marketers refine segments, test personalization strategies, and improve ROI over time.
In short, a CDP works like a continuous engine: collect, connect, activate, learn, and repeat. The real-time nature of this cycle is what turns passive data into proactive marketing fuel.
CDP vs CRM vs DMP: What’s the Difference?
Marketers often ask where a Customer Data Platform (CDP) fits within the broader marketing technology (MarTech) ecosystem. Is it simply a more advanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system? Or a modern alternative to a Data Management Platform (DMP)? In reality, CDPs serve a different, more strategic role..
| Platform | Primary Function | Key Limitation | CDP Advantage |
| CRM | Manages known customer interactions (e.g., sales, support) | Doesn’t unify behavioral data across platforms | CDPs bring behavioral and transactional data together for richer insights |
| DMP | Handles anonymous third-party data for advertising | Outdated in a post-cookie world | CDPs focus on first-party, privacy-compliant data |
| Data Warehouse | Stores massive datasets for reporting | Not built for marketing activation or real-time use | CDPs make data actionable across touchpoints |
| Marketing Automation Platform (MAP) | Automates campaigns like email journeys | Doesn’t unify data from all sources | CDPs fuel MAPs with rich, real-time profiles |
Instead of replacing these tools, CDPs enhance them—acting as the data infrastructure that fuels better decisions and personalization at scale.
To learn more, refer to our detailed blog about the key differences between CDP vs Data Warehouse.
Why CDPs Are on the Rise — and Essential for Customer Engagement
The demand for Customer Data Platforms is surging, driven by the convergence of tighter privacy regulations, growing personalization expectations, and mounting pressure on marketing efficiency.
As third-party cookies phase out, first-party data has become marketing gold. CDPs excel in this landscape by helping brands collect, unify, and act on data in a compliant, privacy-first way. They bridge the gap between fragmented data systems and deliver enriched, real-time profiles that marketers can use immediately—no engineering wait times, no data silos.
Here’s why CDPs are rising in popularity:
- Shift to first-party data: With growing restrictions on third-party data, CDPs provide a secure and compliant way to harness valuable first-party data.
- Demand for personalization: 91% of marketing leaders say cross-channel personalization is key to retention. CDPs power this by enabling real-time segmentation and activation.
- Efficiency under pressure: Marketing budgets are under scrutiny. CDPs reduce tech sprawl by consolidating data and streamlining execution.
- Real-time activation: Marketers can automate actions based on live customer behavior—like triggering cart abandonment messages or showing tailored content.
- Smarter, proactive marketing: With predictive insights and unified profiles, CDPs help teams anticipate needs instead of reacting.
Ultimately, CDPs unify tools, teams, and tactics into one cohesive engine for intelligent, scalable customer engagement.
Core Features to Look for in a Customer Data Platform

Not all CDPs are created equal. To choose the right one for your business, it’s critical to understand what core features to look for and how they impact your ability to deliver personalized, data-driven marketing.
Here’s a checklist of essential CDP features to prioritize:
- Real-time Data Ingestion & Normalization: Your CDP should be able to collect structured and unstructured data across all customer touchpoints in real time (web, app, POS, CRM) and normalize it for unified use.
- Cross-Device Identity Resolution: Look for robust identity resolution that unifies customer behavior across devices and channels using cookies, logins, emails, and more.
- Visual Segment Builder: Empower marketers to create, adjust, and test audience segments with a drag-and-drop UI without requiring SQL or technical skills.
- Consent & Privacy Management: Ensure your CDP can capture and respect consent preferences in compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy laws.
- Marketing Activation Connectors: Your CDP should plug into all key execution tools (email, SMS, ad platforms, push notifications) so you can act on insights immediately.
- Predictive Scoring & Affinity Modeling: Leading CDPs use machine learning to surface valuable signals like churn risk, likelihood to convert, or product affinity scores.
- Generative AI Capabilities: Emerging platforms are starting to include generative AI to assist with content creation such as personalized product recommendations or email copy at scale.
- Real-Time Personalization: AI-enabled CDPs can dynamically update customer profiles and personalize messaging as behaviors unfold.
- Reporting & Dashboarding: Built-in analytics should help you understand audience trends, segment performance, and overall campaign effectiveness without needing to export data.
When evaluating vendors, use this checklist to compare options apples-to-apples and ensure you’re choosing a platform that supports both your current goals and future growth.
To learn more about how these features drive real growth, read our blog on the benefits of real-time customer data platform.
CDP Use Cases by Industry
CDP ROI Across Use Cases
Beyond industry-specific examples, CDPs deliver measurable business impact. Here are key performance metrics marketers often use to quantify ROI:
- Engagement Rates: Higher open and click-through rates from personalized, behavior-based messaging
- Conversion Rates: Improved outcomes from targeted campaigns and predictive scoring
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Smarter segmentation reduces wasted ad spend
- Customer Retention: Better lifetime value through proactive churn management
From personalized shopping to retention-focused messaging, CDPs prove their value across verticals by helping marketers connect the dots and the data with real business results.
Customer Data Platforms aren’t one-size-fits-all—they’re adaptable solutions that solve specific marketing challenges across different industries. Let’s look at how CDPs deliver impact in four sectors: Retail & Ecommerce, Media & Streaming, Finance, and Travel.
Retail & Ecommerce
Retail marketers juggle fast-changing inventory, shifting consumer preferences, and competitive pressure from marketplaces. A CDP helps unify online and offline data from browsing behavior to in-store purchases so brands can create hyper-relevant experiences.
Use Cases:
- Product affinity modeling for personalized recommendations
- Real-time cart abandonment emails or push notifications
- Loyalty tier targeting and engagement
Customer Success Example: CarParts.com
“Blueshift’s platform flexibility addresses our complex data structure and makes it simple to deliver personalized messages and grow our channels. The people behind Blueshift really care about our success and are one of the main reasons we’re at where we are today.”
— Houman Akhavan, Chief Marketing Officer, CarParts.com
CarParts.com, a leading online auto parts retailer, transformed its marketing strategy by leveraging Blueshift’s CDP to personalize recommendations and automate multi-channel campaigns. They replaced batch-and-blast tactics with dynamic campaigns tailored to each user’s vehicle type and browsing history. This included cart abandonment, post-purchase upsell, and category-based messaging across email and SMS.
Results:
- 400% increase in click-through rates
- 130% growth in message volume
- 50 hours saved weekly by removing engineering dependencies
Media & Streaming
For publishers and platforms, engagement is everything. CDPs enable them to tailor content recommendations and ad experiences based on nuanced consumption habits.
Use Cases:
- Watch history-based show recommendations
- Predictive churn scoring to retain subscribers
- Personalized newsletters based on article engagement
Customer Success Example: U.S. News & World Report
“Once you have all this data integrated within the CDP, there is so much functionality available in there that you don’t need engineers to go and customize something for you… it’s very, very helpful for the marketers.”
— Vineet Mahajan, CTO, U.S. News & World Report
U.S. News & World Report used Blueshift’s CDP to unify and activate customer data across platforms—without relying on IT. By combining real-time behavioral data with warehouse insights, they empowered marketing teams to independently build segments and run AI-powered campaigns. The result? Stronger engagement, faster campaign execution, and true data democratization across the organization.
Finance
Finance brands must balance personalization with compliance and risk mitigation. CDPs can help trigger educational journeys, detect unusual behavior, and improve communication relevance.
Use Cases:
- Onboarding journeys based on user type
- Fraud detection signals flagged through behavioral anomalies
- Financial education content tailored by transaction behavior
Customer Success Example: Ent Credit Union
“The biggest efficiency we gained is around segmentation. Previously, it would take about 25 hours of work time, usually about two calendar weeks, to identify an audience and get an approved audience back. Now, we do it in minutes.”
— Ben Savage, Director of Digital Marketing, Ent Credit Union
Ent Credit Union partnered with Blueshift to unify and activate all of their rich member data. With unified member profiles and marketer-friendly tools for audience targeting and cross-channel campaign orchestration, Ent Credit Union delivers personalized digital experiences that resonate with each member, leading to a 32% increase in member engagement.
Travel & Hospitality
Travel brands thrive on timing and context. A CDP helps them anticipate needs and deliver offers at just the right moment, whether someone is researching a trip or lounging at their hotel.
Use Cases:
- Real-time offer personalization based on search and booking behavior
- Loyalty program segmentation and upsell opportunities
- Geo-personalized mobile messages for on-property services
Customer Success Example: Zumper
“About half a million apartments live on the site at any point and we’re expecting close to 100 million users. We use Blueshift AI to match people and apartments, and send users the right apartments at the right time through the right campaigns.”
— Russell Middleton, Co-Founder, Zumper
Zumper used Blueshift’s CDP to match renters with listings based on real-time preferences like price, location, and amenities. The platform’s AI-driven recommendations, behavior-based triggers, and automated testing helped Zumper scale its marketing across channels without adding headcount.
Results:
- 384% increase in lead submissions
- 198% increase in message volume
- 128% increase in click-through rates
From personalized shopping to retention-focused messaging, CDPs prove their value across verticals by helping marketers connect the dots and the data.
How to Implement a Customer Data Platform (Without Chaos)
Implementing a CDP is a strategic initiative—one that requires planning, alignment, and a clear roadmap to avoid chaos. Here’s how marketers can do it right.
1. Audit Your Current Data Ecosystem
Start by mapping out all your current data sources—CRM, website, email platform, POS system, mobile app, support channels, and more. Identify where customer data is stored, how it’s formatted, and who owns each system. This audit helps uncover both opportunities and gaps.
2. Define Use Cases and Customer Journey Goals
Don’t implement a CDP just to say you have one. Outline your primary goals first: Do you want to reduce cart abandonment? Improve retention? Enable real-time segmentation? Having use cases mapped to business outcomes will guide your implementation priorities.
3. Align Marketing, IT, and Data Teams from Day One
A successful rollout hinges on cross-functional collaboration. Marketing, IT, and analytics stakeholders must work together from the start to evaluate data architecture, plan integrations, and set governance standards. CDPs that lack internal ownership or alignment often stall before they generate value.
4. Assess Internal Readiness
Before diving in, assess whether your organization has the internal resources, skills, and cultural buy-in to support a CDP. Do you have team members who understand customer data? Are your marketing strategies mature enough to take full advantage of personalization at scale? Clarifying this upfront can save time and reduce rework.
5. Clean and Standardize Incoming Data
Dirty data is the enemy of personalization. As you prepare for integration, cleanse your existing data to remove duplicates, standardize naming conventions, and ensure consistent formatting. This step is crucial for building accurate profiles and segments.
6. Start with a Pilot Use Case
Choose one high-impact, measurable use case to pilot; such as a cart abandonment flow or onboarding campaign. Test how data flows, how segments behave, and how activation performs. Use this to refine workflows before expanding.
7. Monitor, Optimize, and Scale
Once your CDP is live, don’t set it and forget it. Track performance metrics, analyze data quality, and iterate your segmentation strategies. Scale gradually to additional channels and use cases based on what’s working.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Over-Customization: Trying to create a bespoke CDP architecture often leads to delays and maintenance issues.
- Lack of Ownership: Without clear leadership and cross-functional ownership, CDP projects can stall. Assign internal champions.
- Ignoring Compliance: Data governance and privacy regulations must be baked into your implementation process.
Implementing a CDP is less about flipping a switch and more about building an ecosystem. With the right foundation, internal readiness, and phased approach, marketers can unlock serious value, without the chaos.
CDP Trends and the Future
The world of CDPs is evolving fast, driven by rising consumer expectations, increasing data complexity, and the growing influence of artificial intelligence. To stay competitive, marketers need to understand not just today’s capabilities, but the innovations shaping the future of these platforms.
Here’s what’s next for CDPs:
- Composable CDPs: These cloud native architectures offer modularity and flexibility. Instead of relying on a rigid, all in one solution, businesses can mix and match best in class components, such as data ingestion, identity resolution, or activation, based on their specific needs.
- CDPs Inside Customer Engagement Platforms: Today’s most advanced Customer Engagement Platforms (CEPs) often embed CDP functionality at their core, bringing together data and decisioning in a single platform. These AI powered CDPs don’t just centralize customer information, they continuously process it to:
- Score leads based on engagement and buying signals
- Recommend the right content or offer for each user
- Predict churn and proactively retain at risk customers
- Suggest next best actions to improve outcomes across the journey
- Generative AI: Beyond analytics, generative AI enables marketers to auto create dynamic, personalized content, from product recommendations to email copy, enhancing campaign speed and engagement.
- Cross Departmental Adoption: Once a marketing only tool, CDPs are now used across product, support, and executive teams. Shared insights drive better decision making organization wide.
- Ecommerce Integration: Expect deeper support for conversational commerce, dynamic storefront personalization, and behavior triggered offers across digital shopping experiences.
- Privacy by Design: Future ready CDPs embed governance and consent into the data architecture, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA without sacrificing personalization.
- Edge Computing Capabilities: CDPs are beginning to support personalization at the edge, delivering real time, localized experiences within browsers and apps without server latency.
In short, tomorrow’s CDP will be modular, AI native, privacy first, and enterprise wide, empowering brands to shift from reactive marketing to predictive, proactive, and truly personal engagement.
Blueshift’s Customer Data Platform: A Real-Time Engine for Smarter Marketing

Blueshift’s CDP is designed to help marketers unify and activate first-party data with ease. It brings together customer behavior across touchpoints into a single, dynamic profile, powering personalized engagement, adaptive segmentation, and measurable growth.
Dynamic Customer Profiles
Profiles are updated in real time with every new action a customer takes. Whether anonymous or known, Blueshift’s identity resolution stitches together a seamless view across devices and channels. Flexible data structures mean there is no need for costly customization.
Build Precise, Predictive Segments
Easily create audience segments based on behavior, affinity, lifecycle stage, or predicted intent. Segments update automatically and are ready to activate across all channels.
- Target high propensity buyers
- Reengage likely churners
- Tailor campaigns based on loyalty or transaction history
Real-Time Personalization
Blueshift enables content blocks and product recommendations to adapt instantly to each customer’s latest behavior. From trending items to next best actions, it is all powered by up-to-the-minute data.
Audience Insights Without SQL
Access deep cohort and segment-level analysis without relying on data teams. Easily visualize impact and optimize budget allocation with intuitive dashboards.
Connect Your Entire Stack
With native integrations to email, mobile, web, and advertising tools, Blueshift unifies marketing orchestration and data activation, so teams can move fast, intelligently.
Built-In Privacy and Security
Blueshift complies with GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and SOC2, offering enterprise grade encryption, consent management, and role based access to protect your customer data.
The Future of Marketing Starts with Unified Data
Customer expectations aren’t slowing down, and neither should your marketing.
As consumers demand more personalization, speed, and consistency across channels, fragmented data stacks are no longer sustainable. A Customer Data Platform doesn’t just fix these gaps; it unlocks a new level of agility, intelligence, and impact. From real-time personalization to AI-powered predictions and privacy-first architecture, CDPs are built for the modern marketer’s reality.
This isn’t about chasing the next shiny tool. It’s about building a smarter foundation that empowers your team to launch campaigns faster, target more precisely, and deliver experiences your customers actually value.
If you’re serious about creating marketing that connects, converts, and lasts, the time to invest in a CDP is now.
Ready to see how Blueshift can help? Our Intelligent Customer Engagement Platform (ICE) includes a robust Customer Data Platform as its foundation, working in tandem with cross-channel orchestration and AI to unify your data and activate it throughout the customer journey.
Learn more about Blueshift’s Customer Data Platform